Complete Information About Brain Aneurysm Treatment
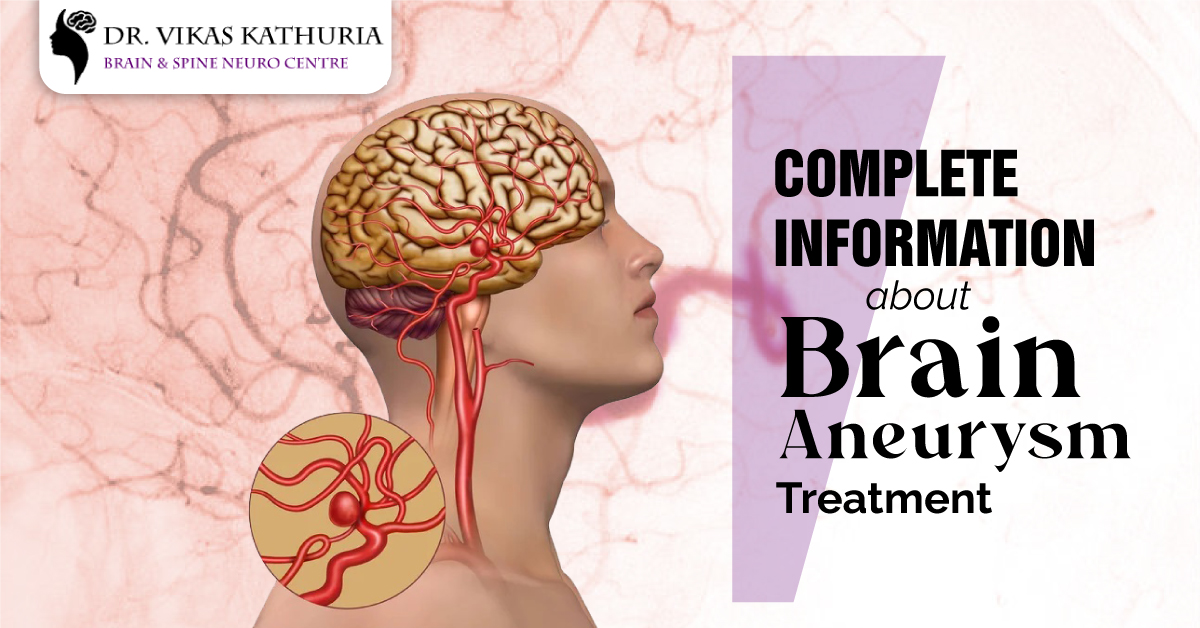
In the case of an aneurysm in the brain, a bulge in a blood vessel develops and fills with blood, causing it to rupture. Aneurysms usually don’t cause symptoms until they rupture and start leaking blood. A ruptured aneurysm can induce a severe headache and even a fatal stroke if left untreated. It is possible to treat an aneurysm by preventing blood from entering the aneurysm and diverting it away from it.
Definition of Aneurysm: What Is It?
As the name suggests, a brain aneurysm (also known as a subarachnoid hemorrhage, or SAH) is a weak area in the wall of a blood vessel in the brain. What does it feel like when you’re looking at a weak point in a balloon? That’s how it feels when you get a brain aneurysm.
This part of the blood vessel expands like a bubble due to the continual blood flow. Smaller than a berry, it can mature into an adult. A wide variety of them exists, including:
The most frequent type of aneurysm in the brain is a saccular aneurysm. The central artery forms a dome-like structure. They are linked to the artery by a tiny “neck.”
Fusiform aneurysms are rarer than saccular ones. They don’t form a dome when they’re compressed. The procedure instead expands the blood vessel.
Despite their startling sound, most brain aneurysms don’t create symptoms or health problems. It’s possible to live a long life and not even be aware of it.
On the other hand, aneurysms can become huge, leak, or even burst under certain conditions. Medical assistance must be sought immediately for a hemorrhagic stroke or bleeding in the brain.
Aneurysms in the brain are rather typical occurrences
As many as 6% of the population in the United States has a brain aneurysm that isn’t leaking blood (called an unruptured aneurysm). Brain aneurysm ruptures are extremely rare. About 30,000 people in the United States experience them each year.
A brain aneurysm can occur in anyone, but who is at risk?
Stenting for Stroke and Brain Aneurysm is more likely to occur if you: 
- Are a woman.
- Are between the ages of 40 and 60.
- There are cases of aneurysms in your family’s medical history.
- An arterial dissection, for example, or fibromuscular dysplasia or cerebral arteritis.
- Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, neurofibromatosis type 1, or Loeys-Dietz syndrome are examples of connective tissue disorders.
- Suffer from polycystic renal disease.
- Have a congenital brain aneurysm.
Causes of Aneurysms in the brain 
A brain aneurysm’s cause is unknown. Blood vessels are thought to be irritated and weakened by several factors:
- Smoking
- There is also a risk of blood infection.
- An elevated heart rate (hypertension).
- Addiction to cocaine and amphetamines.
- Injuries to the brain are caused by traumatic events (often caused by car crashes).
- The disease of arteriosclerosis (fatty buildup on blood-vessel walls).
When do brain aneurysms develop?
People as young as 30 are susceptible to brain aneurysms, but they’re more common after age 40.
What causes aneurysms in the brain to rupture?
It’s still unclear why an aneurysm ruptures or leaks, leading to internal bleeding in the brain. In the end, anything that raises blood pressure can be harmful. Blood is pushed harder against the walls of blood vessels when blood pressure is higher.¬†
- Long-term stress or a quick outburst of rage or other intense emotion might raise blood pressure.
- Lifting, carrying, or pushing something heavy, such as weights or furniture, requires much effort.
- High blood pressure is well-documented but not adequately managed by medication.
Are aneurysms in the brain an unpleasant experience?
Many people are unaware that they have a brain aneurysm that has not yet ruptured. Rarely does it create any discomfort or other symptoms at all?
When looking into the reasons for chronic headaches, many smaller (and not just larger) aneurysms are discovered. Researchers aren’t sure if unruptured aneurysm headaches are linked. In some cases, it is considered that the swelling of the blood vessel is generating a headache by putting pressure on nearby neurons and membranes.
It is possible to have a ruptured aneurysm with a sudden, intense headache (often referred to as a “thunderclap headache”). An aneurysm bleeding a little amount of blood can cause a headache that lasts for days or weeks. The term “sentinel headache” refers to this form of persistent pain. It’s a sign that the aneurysm is about to rupture.
A brain aneurysm can cause a sudden, severe headache, stroke symptoms, or both. A ruptured brain aneurysm necessitates urgent medical care and treatment to save a patient’s life. Discuss the risks and benefits of various treatment and management options with Dr. Vikas Kathuria if you have an unruptured brain aneurysm.
